SBPMD Histology Laboratory Manual
Female Reproductive System: Micrograph
Examine the electron Micrographs so that you understand the ultrastructural equivalents of the structures you have seen under the microscope.
Secondary follicle | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
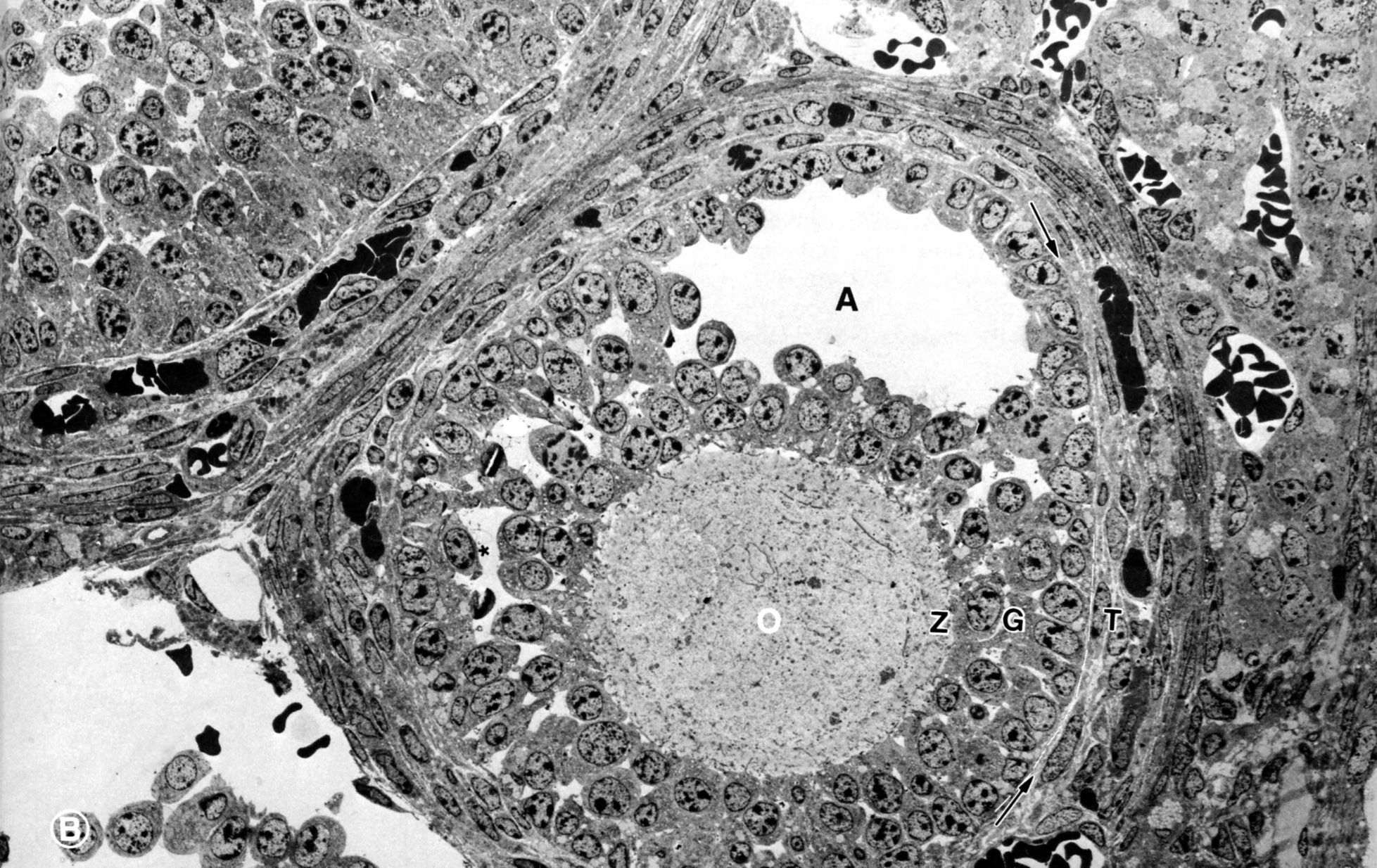 |
The secondary follicle is multilayered and there is an accumulation of follicular fluid, the antrum (A). Fluid filled spaces between granulosa cells (*); granulosa cells (G); oocyte (O); theca folliculi (T); zona pellucida (Z); arrows indicate boundary between granulosa cells and theca interna. Note that the vasculature is outside the theca interna. (ovary, cat) |
| |
Epithelium of Oviduct | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
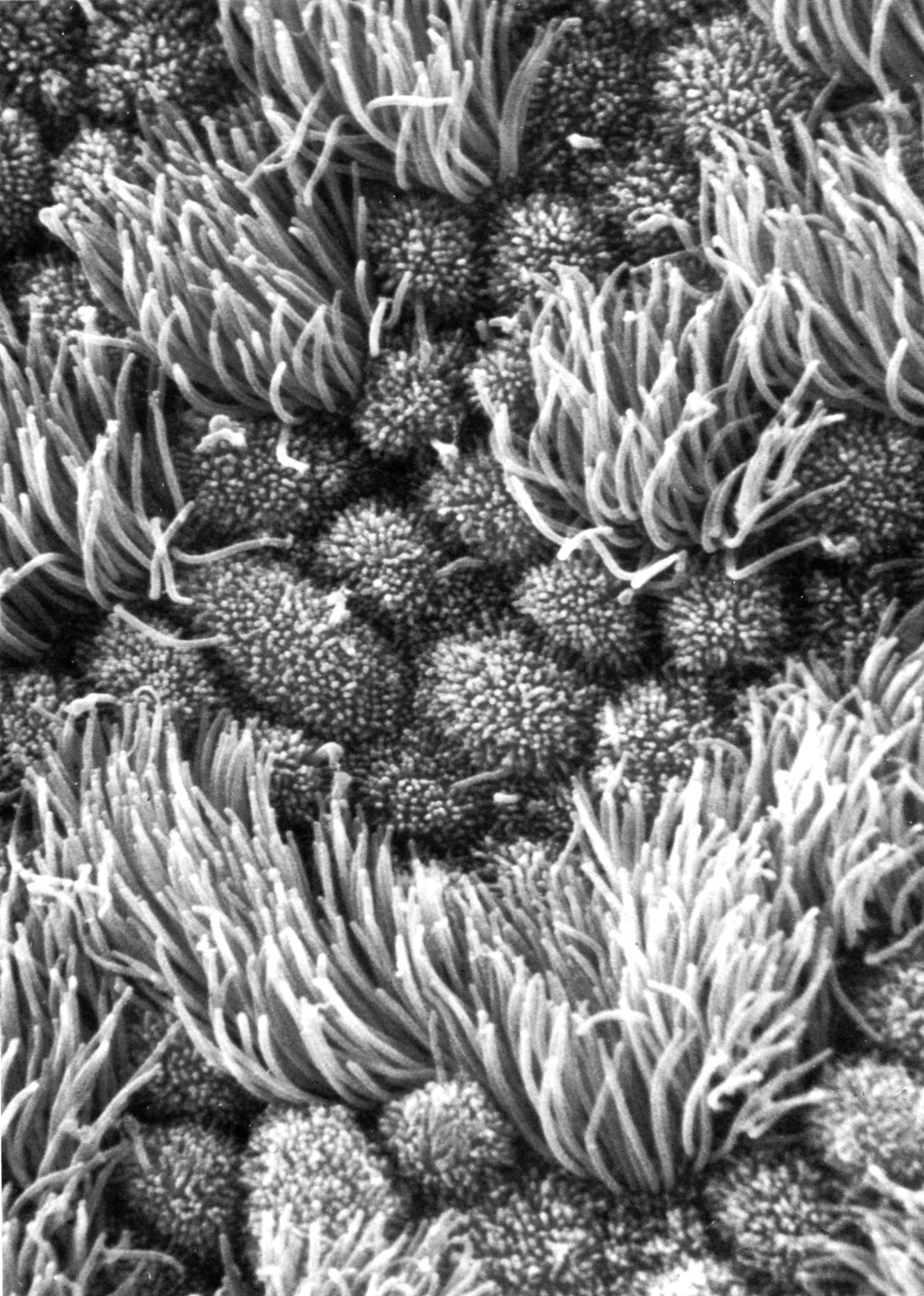 |
Epithelium of oviduct, scanning EM. Human oviduct showing ciliated cells and nonciliated cells (with microvilli). |
| |
Diagram of implantation and placental formation | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
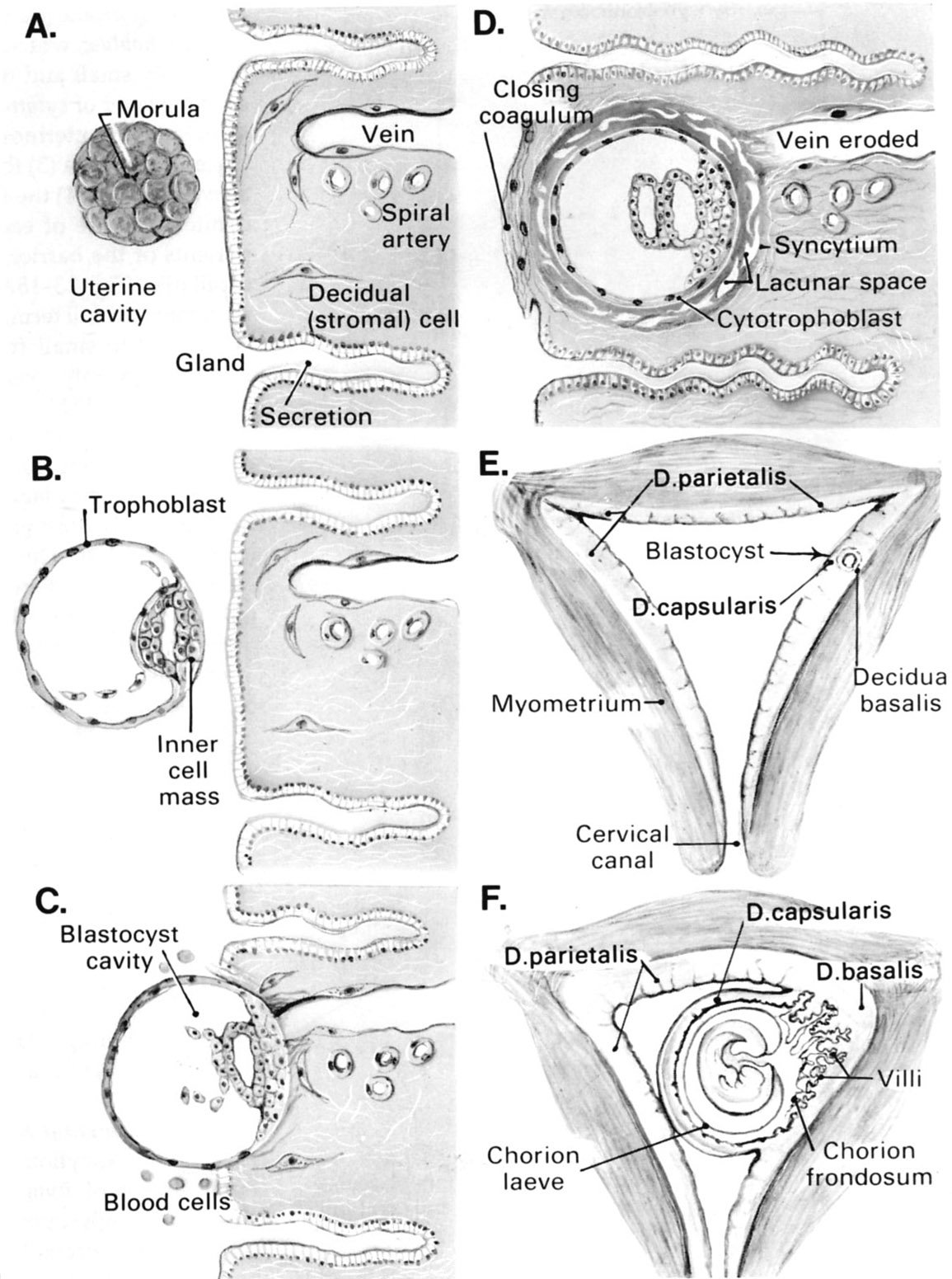 |
Schematic diagram of implantation and development of the fertilized ovum. A, B, C and D illustrate stages in formation of the blastocyst and embedding of the blastocyst in the uterine wall. The relation of the growing embryo to the deciduae of the uterus is shown in E and F. |
| |
Placental barrier between maternal and fetal blood | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
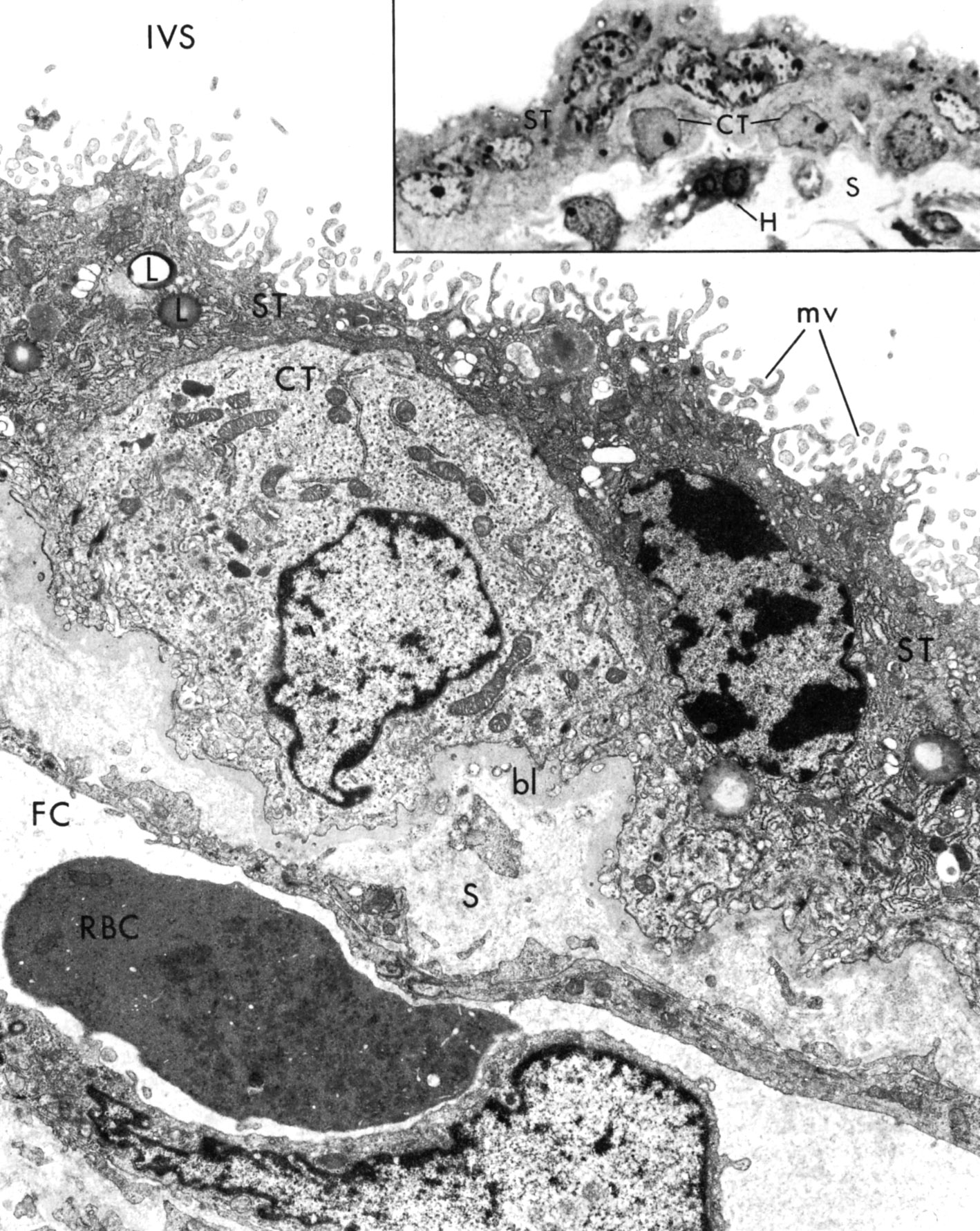 |
Normal human placental barrier at 24 weeks of pregnancy. Photomicrograph at upper right illustrates multinucleate syncytial trophoblast (ST) overlying the cytotrophoblastic cells (CT). The nuclei of the syncytiotrophoblast are more heterochromatic. H, Hofbauer cell, S, fetal stroma.
In the larger micrograph the barrier between maternal and fetal blood can be seen: syncytiotrophoblast, cytotrophoblast, basal lamina, fetal capillary endothelium. Cytotrophoblast cells (CT) act as stem cells for the syncytiotrophoblast (ST) The syncytiotrophoblast contains an abundance of RER, pleomorphic microvilli (mv), lipid droplets (L), and membrane-limited granule. The basal lamina (bl) is thick). Fetal stroma (S); fetal capillary (FC); RBC, fetal red blood cell (RBC) with mitochondria and ribosomes; intervillous space (IVS) |