SBPMD Histology Laboratory Manual
Adrenal Gland
Each of the paired adrenal glands is in fact two glands. The outer mesodermally derived cortex is composed of cells that secrete steroid hormones. The neural crest-derived cells of the medulla secrete catecholamines. The latter are innervated by preganglionic fibers of the sympathetic nervous system.
#72 Adrenal, Monkey, bichromate fixation
Open with WebViewer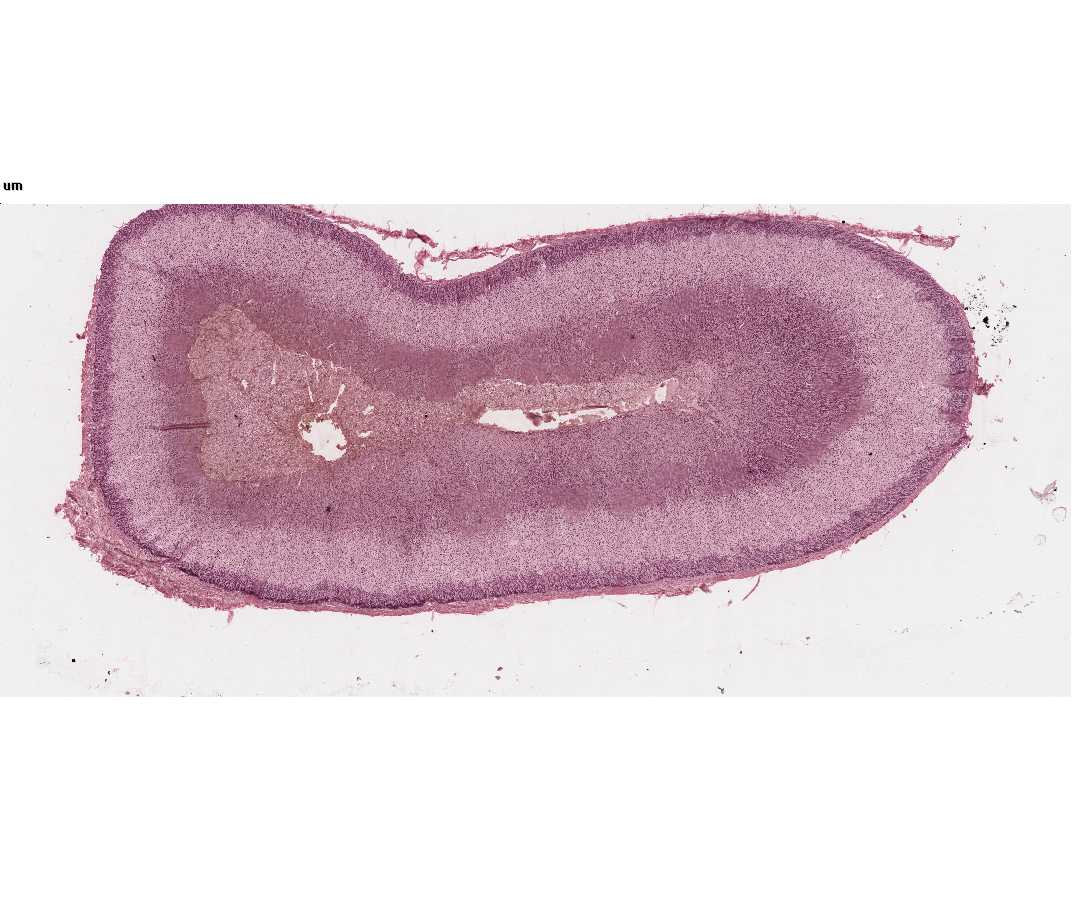
This slide illustrates clearly the classical zonation of the adrenal gland. With the naked eye you should be able to distinguish 5 zones in your section: 1) the outer connective tissue capsule, 2) a thin zona glomerulosa just beneath this, 3) the wide zona fasciculata, 4) a thin zona reticularis, 5) the central medulla, within which lies the large central vein.
Study the various zones in detail at higher magnification.
- The outer connective tissue capsule: The fibrous capsule is supplied with many small arteries, which pierce it and empty into the enlarged fenestrated capillaries (cortical sinusoids) of the adrenal cortex. You may also see small nerves.
- The cells of the zona glomerulosa are arranged in loops and arcades 1-2 cells thick. The nuclei are round and the cytoplasm may contain a few lipid droplets, which will appear as lipid vacuoles.
- The zona fasciculata is made up of columns of large polyhedral cells. The nuclei are round and larger than those of the zona glomerulosa or zona reticularis. The cytoplasm appears frothy or spongy because of the many lipid droplets that have been removed during processing of the tissue.
- The zona reticularis consists of a branching and anastomosing network of polyhedral cells smaller than those of the zona fasciculata. Various degrees of nuclear condensation may be found. The cytoplasm may contain brown lipochrome pigment.
- The medulla is composed of cells that are also arranged in the typical fashion of endocrine glands, cords and clumps of cells surrounded by fenestrated medullary sinusoids. The medullary cells do not have lipid vacuoles, but if fixation is not prompt autodigestion vacuoles may appear in the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm will have a very fine brown granulation due to the chromaffin reaction. The chromaffin reaction is the oxidation of the catecholamines with dichromate salts. Cells making norepinephrine stain darker than those making epinephrine. In the center of the medulla lies the large muscular-walled central vein. The muscle fibers are arranged longitudinally.
#71 Adrenal, Human, bichromate fixation
Open with WebViewer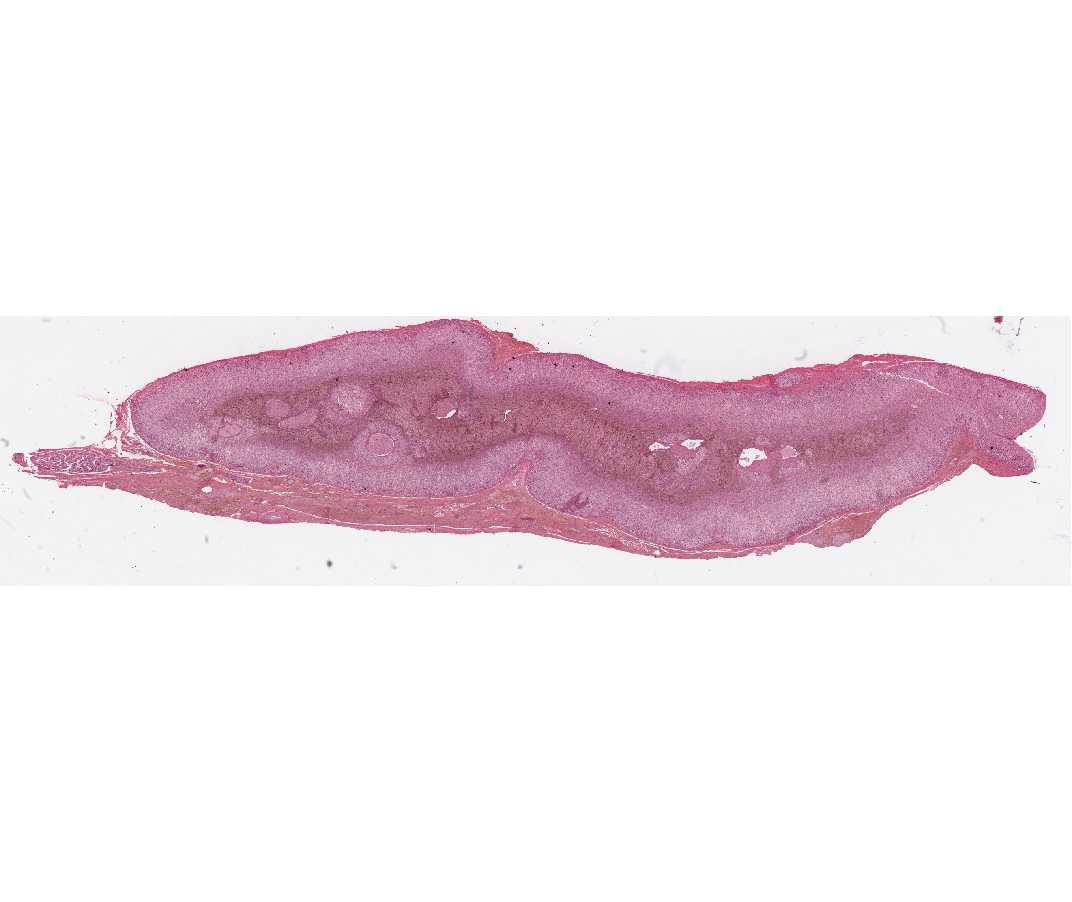
You should study this slide in the same way as #72. The cortical zones are not as clearly demarked. The tissue surrounding the central vein may not be medullary but instead may be in growths of cortical tissue. The chromaffin reaction following bichromate fixation results in differential staining of epinephrine and norepinephrine cells, the latter are stained more darkly brown. In some sections there are nerve bundles in the medulla. These are the preganglionic sympathetic fibers.
What hormone is produced by the zona glomerulosa? By the zona fasciculata? By the zona reticularis? By the medulla? What hormones regulate the function of the cortex? How is medullary function regulated?