SBPMD Histology Laboratory Manual
Skin: Micrographs
Examine the electron Micrographs so that you understand the ultrastructural equivalents of the structures you have seen under the microscope.
Trachea (human) | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
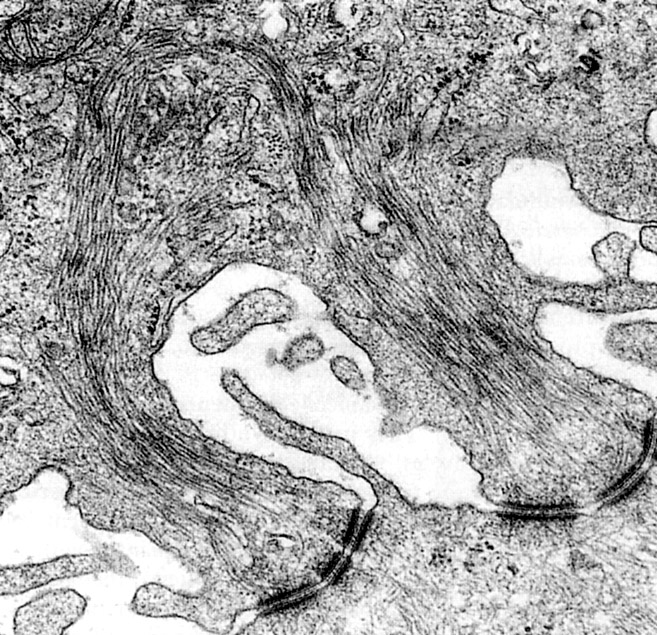 |
Desmosomes. The stratum spinosum of skin epithelium has conspicuous desmosomes. Intermediate filaments (keratin in epithelium) are associated with desmosomes. |
| |
Desmosomes in Stratum Spinosum | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
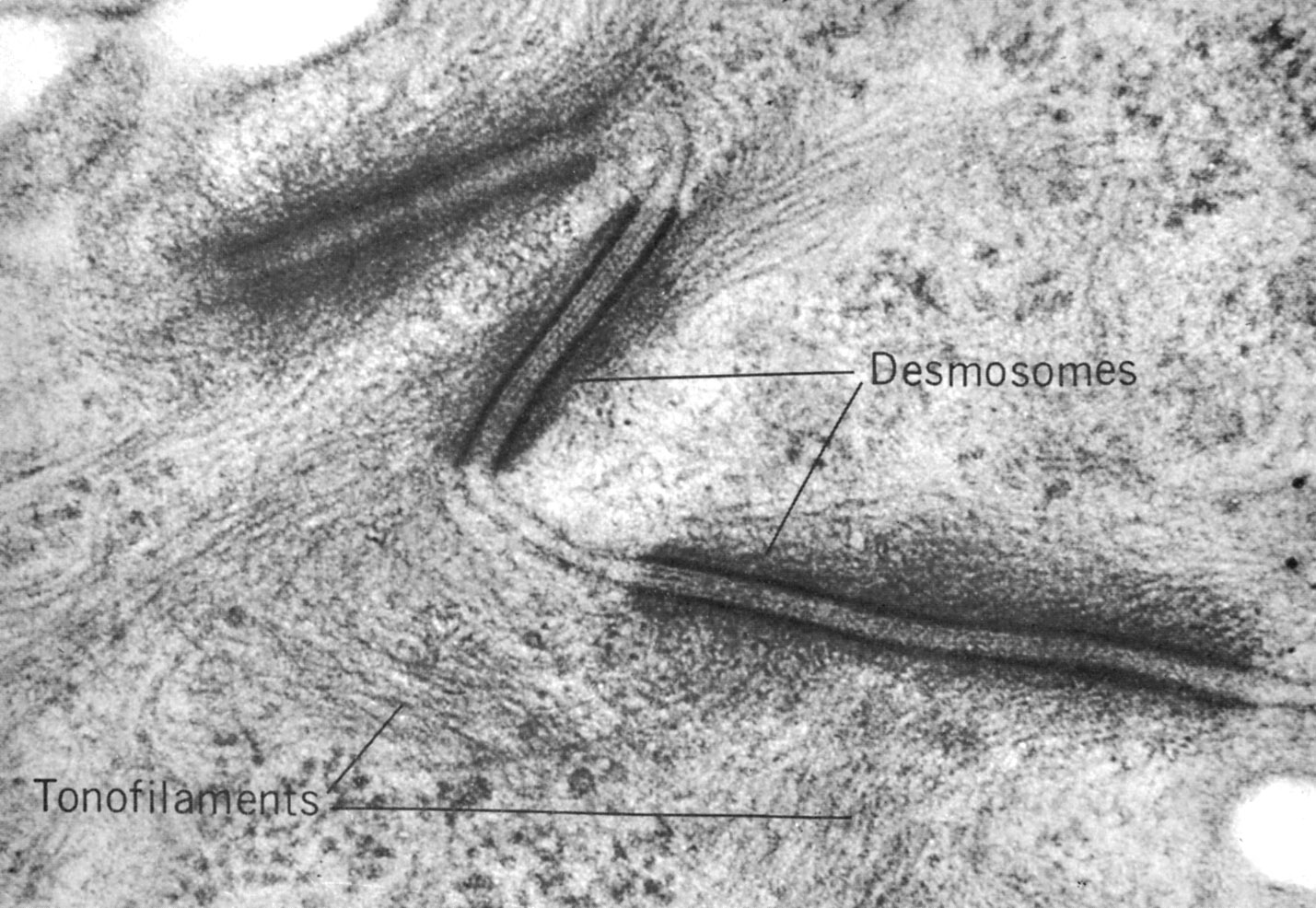 |
Desmosomes in stratum spinosum (hamster cheek pouch epithelium). Tonofilaments (keratin) fill the cells and insert into attachment plaques, intracellular disk-shaped structures containing desmoplakins and plakoglobins. The intercellular space contains the intermediate line containing transmembrane glycoproteins, the desmogleins and desmocollins (members of the cadherin family of calcium dependent adhesion molecules). |
| |
Hemidesmosomes | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
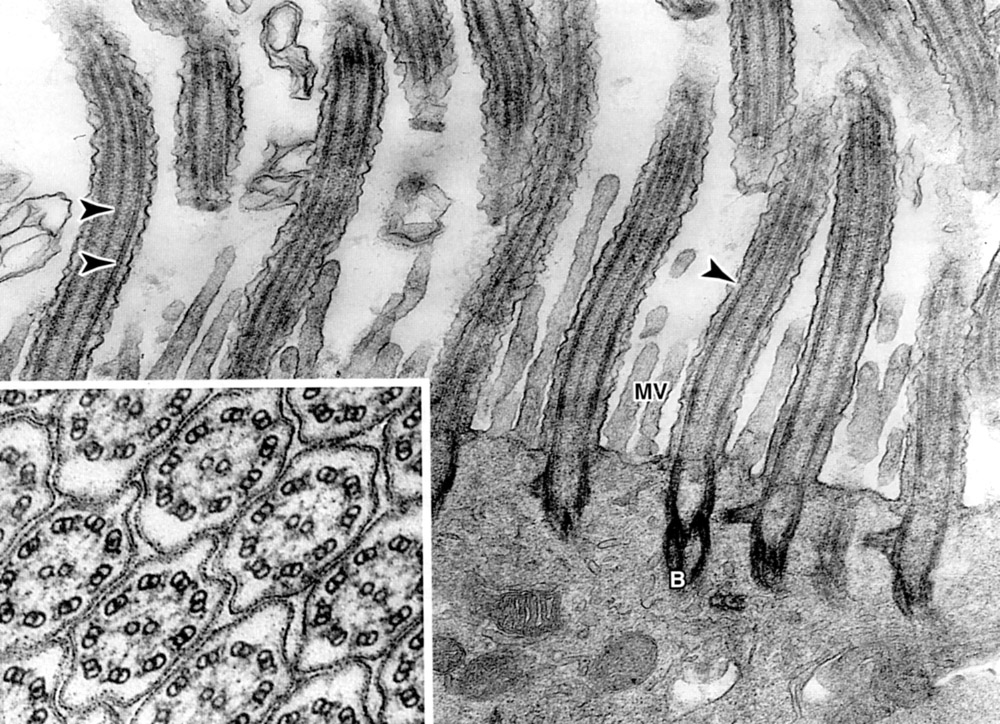 |
Hemidesmosomes in the basal portion of stratum basalis (hamster cheek pouch epithelium). The intracellullar attachment plaque is similar to that in desmosomes, but the transmembrane proteins are integrins that act as receptors for laminin and type IV collagen. |
| |