SBPMD Histology Laboratory Manual
Respiratory System
Open with WebViewer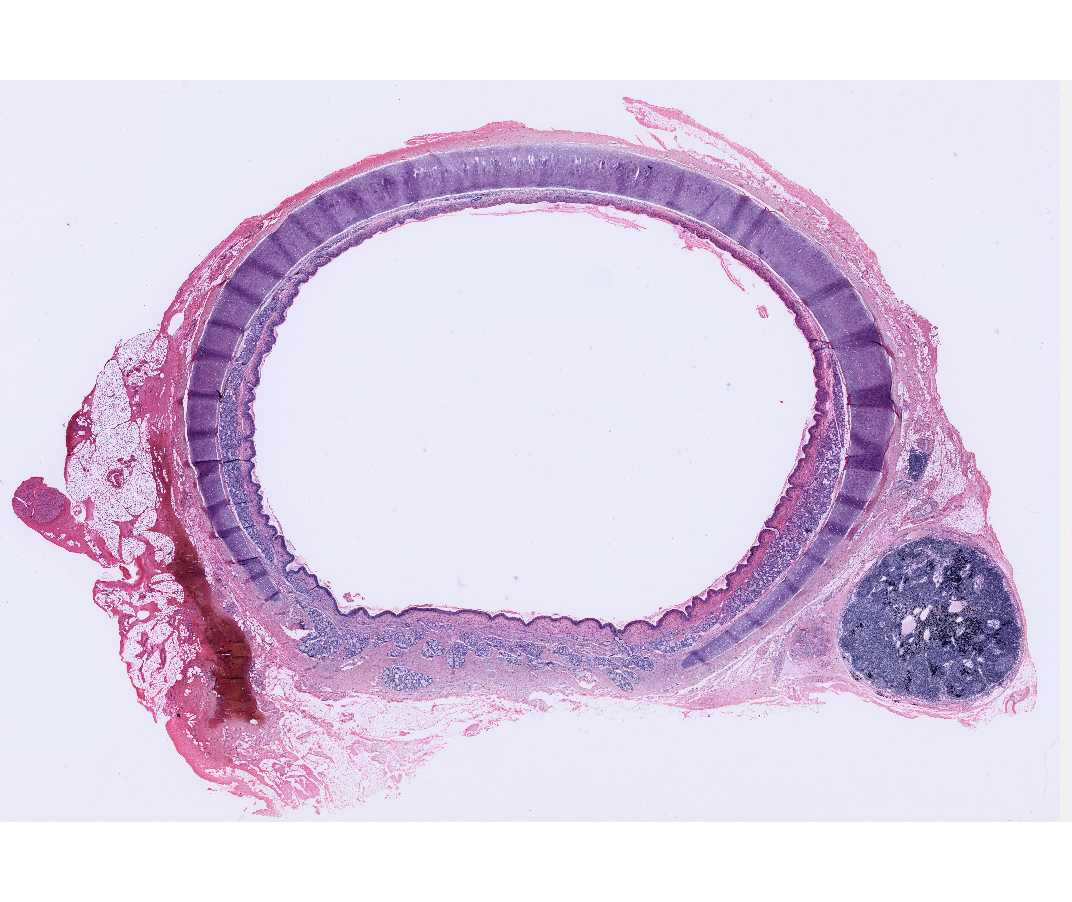
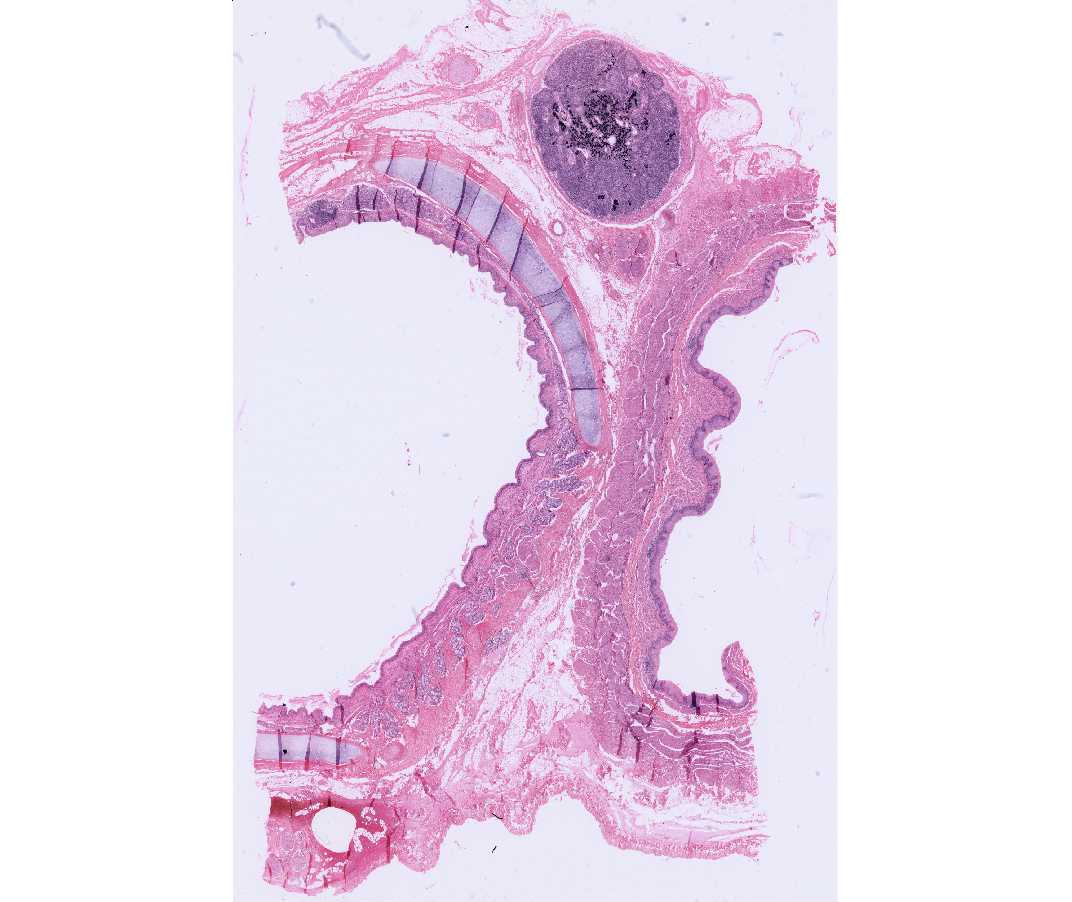
Sections of the trachea are shown and the esophagus may be included. Note the hyaline cartilage in the wall of the trachea and the lining of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium. Cilia are clearly seen in some areas but goblet cells may not be obvious. Exocrine glands are found beneath the epithelium. Lymph nodes and diffuse, sub-epithelial lymphatic tissue are seen. Note also the nerves, blood vessels and adipose tissue. This is a good slide to review these structures.
#88 Trachea and Esophagus
Open with WebViewerLook for the same structures in this slide and the following slide. What criteria do you use to distinguish between the esophagus and the trachea?
#109 Trachea and Esophagus, Rabbit (not scanned)
The pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium lining the trachea in this species is reduced as compared to the human.
#89 Lung, Rabbit H&E
Open with WebViewer
An intrapulmonary bronchus may be included in some sections and is identified by irregularly shaped cartilage plates in its wall. Bronchioles, terminal bronchioles, respiratory bronchioles, and alveoli should be identified. Alveolar ducts, and alveolar sacs may also be seen. Compare the epithelial linings of each of these portions of the respiratory tree and compare them to blood vessels.
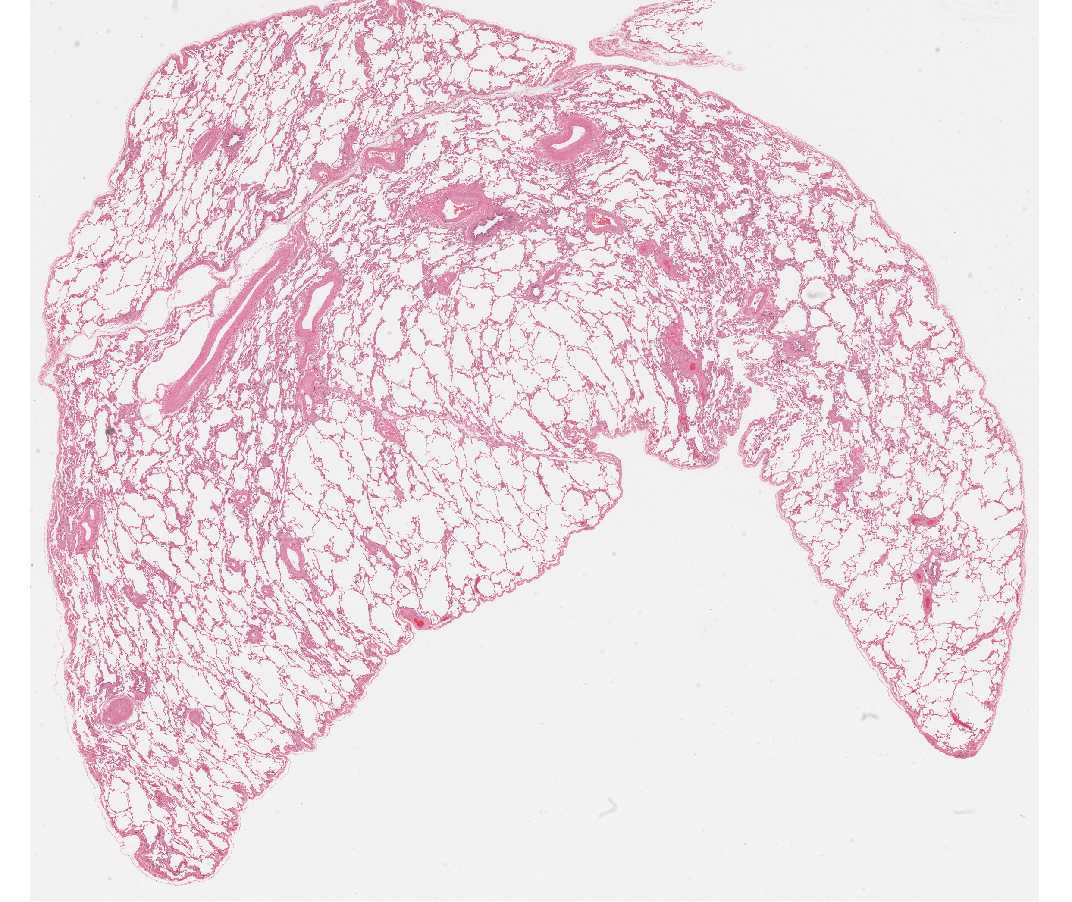
#118 Lung, Human H&E
Open with WebViewerThis lung slide is useful for examining larger portions of the respiratory tree and the vascular system. The alveoli are somewhat collapsed. Their structure is best studied in the following slide.
#105 Lung, Bat, Azure A and Eosin
This is a thin section, which clearly demonstrates cell types seen in the alveoli. Look for an area in which the alveolar walls are in tact. Note the close contact of the smallest capillaries (one red blood cell in diameter) and the simple squamous epithelium lining the alveolus. Gas exchange between blood and air occurs here. Although it is difficult to distinguish type I pneumocytes from endothelial cells, you can identify type II pneumocytes (surfactant cells) and macrophages (dust cells). These latter are frequently found along the wall of the alveolus, or free within the alveolar space. Surfactant secreting giant cells (type II pneumocytes) are present in the epithelium lining the alveolus.
Be sure you know the types of cells found in the alveolus and how they can be distinguished on the basis of fine structure. Know the function of each cell type. Use TEMs to identify cell types and to aid in understanding the structure of the alveolar wall.
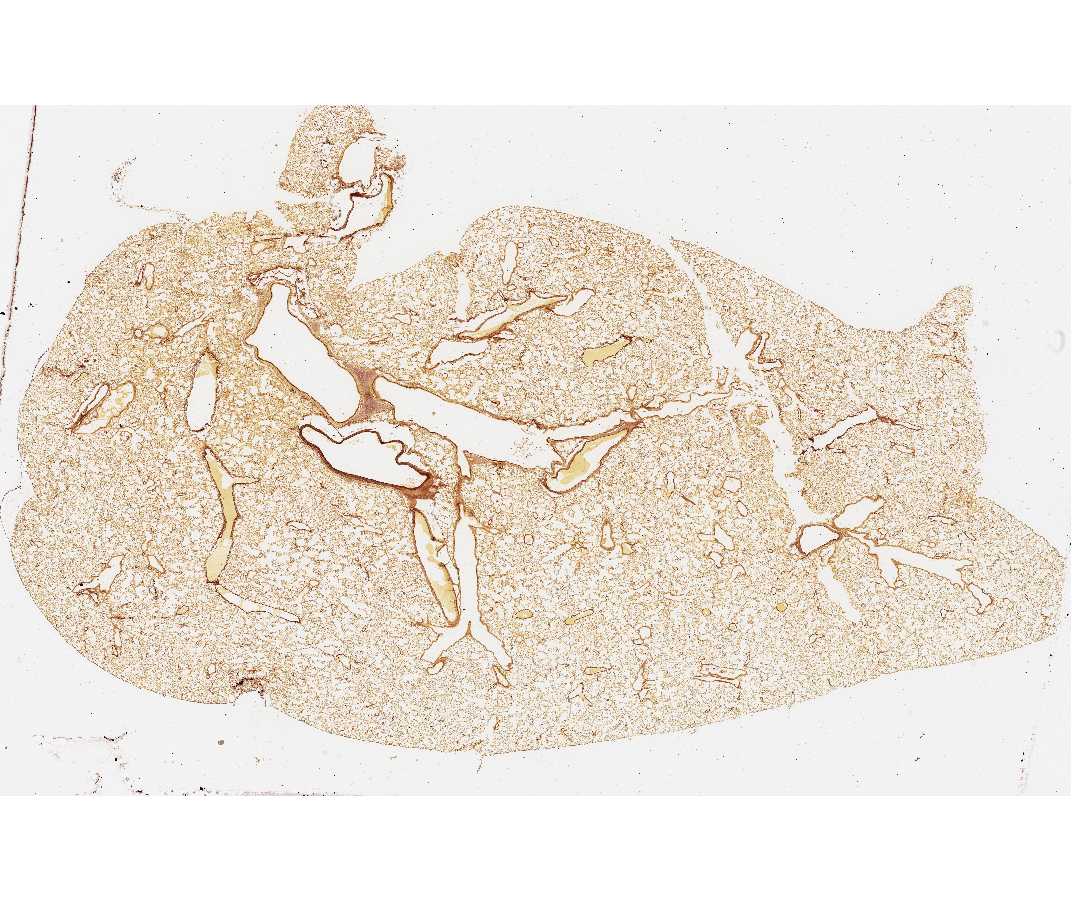
#110 Lung Rabbit Orcein - Van Gieson - Paraffin section 6µm
Open with WebViewerThis stain highlights the elastic fibers (red brown) in the lung.