SBPMD Histology Laboratory Manual
Muscle: Micrographs
Examine the electron Micrographs so that you understand the ultrastructural equivalents of the structures you have seen under the microscope.
Sarcomere of Skeletal Muscle (mammalian): TEM and Diagram | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
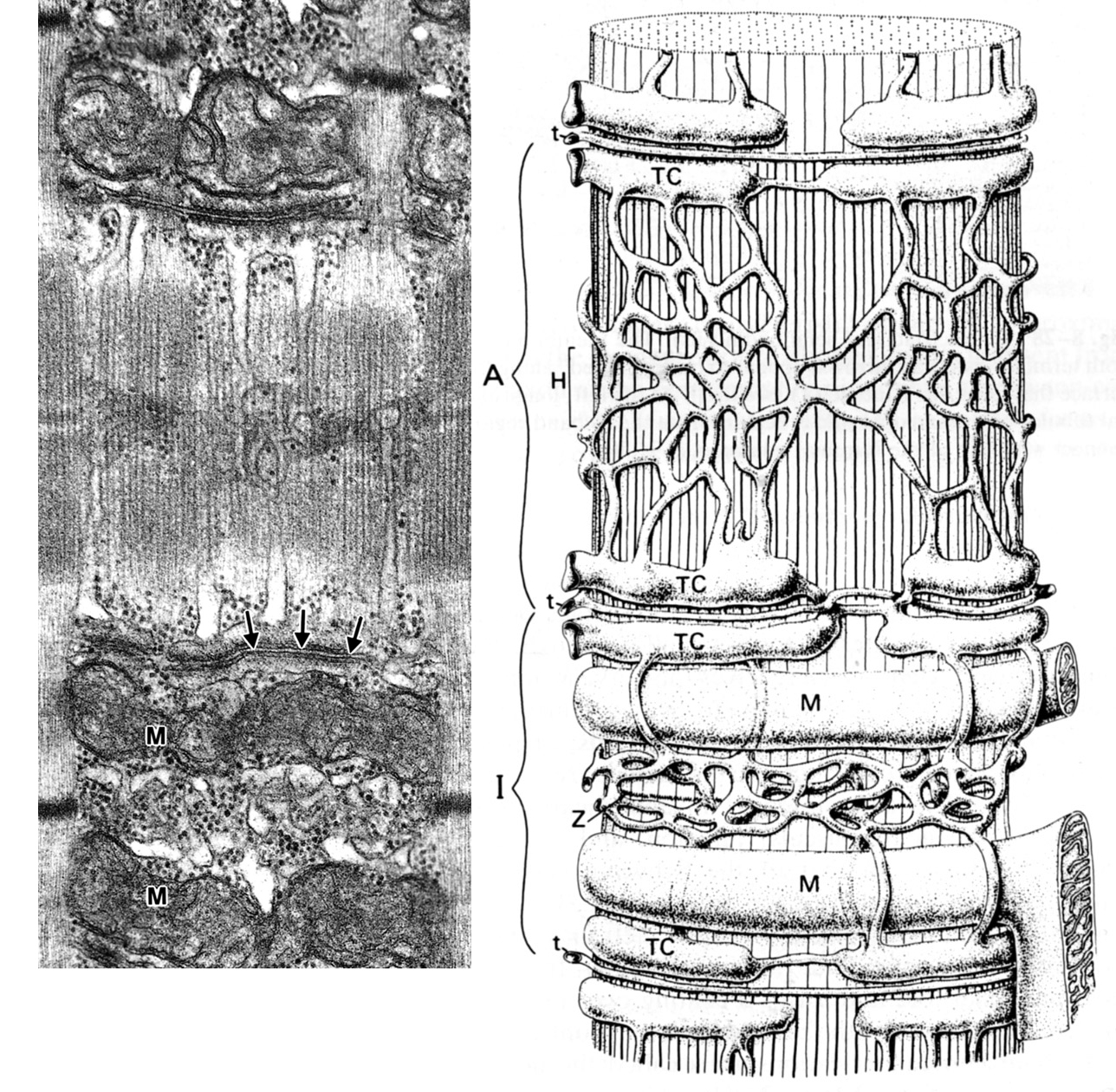 |
Sarcomere of skeletal muscle (mammalian): TEM and diagram. The sarcoplasmic reticulum extends over the A band and into the I band and forms a tubular network in the region of the H band. Longitudinal tubules give rise to terminal cisternae closely associated with the transversely oriented T tubule (arrows). The triads are located near the junction of the A and I bands. The part of the sarcoplasmic reticulum that connects with that of the succeeding sarcomere is incomplete in this plane of section. Portions of it are visible between paired I-band mitochondria (M), which are closely aligned with the triad. (diaphragm, rat) |
| |
Schematic Diagram of Cardiac Muscle | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
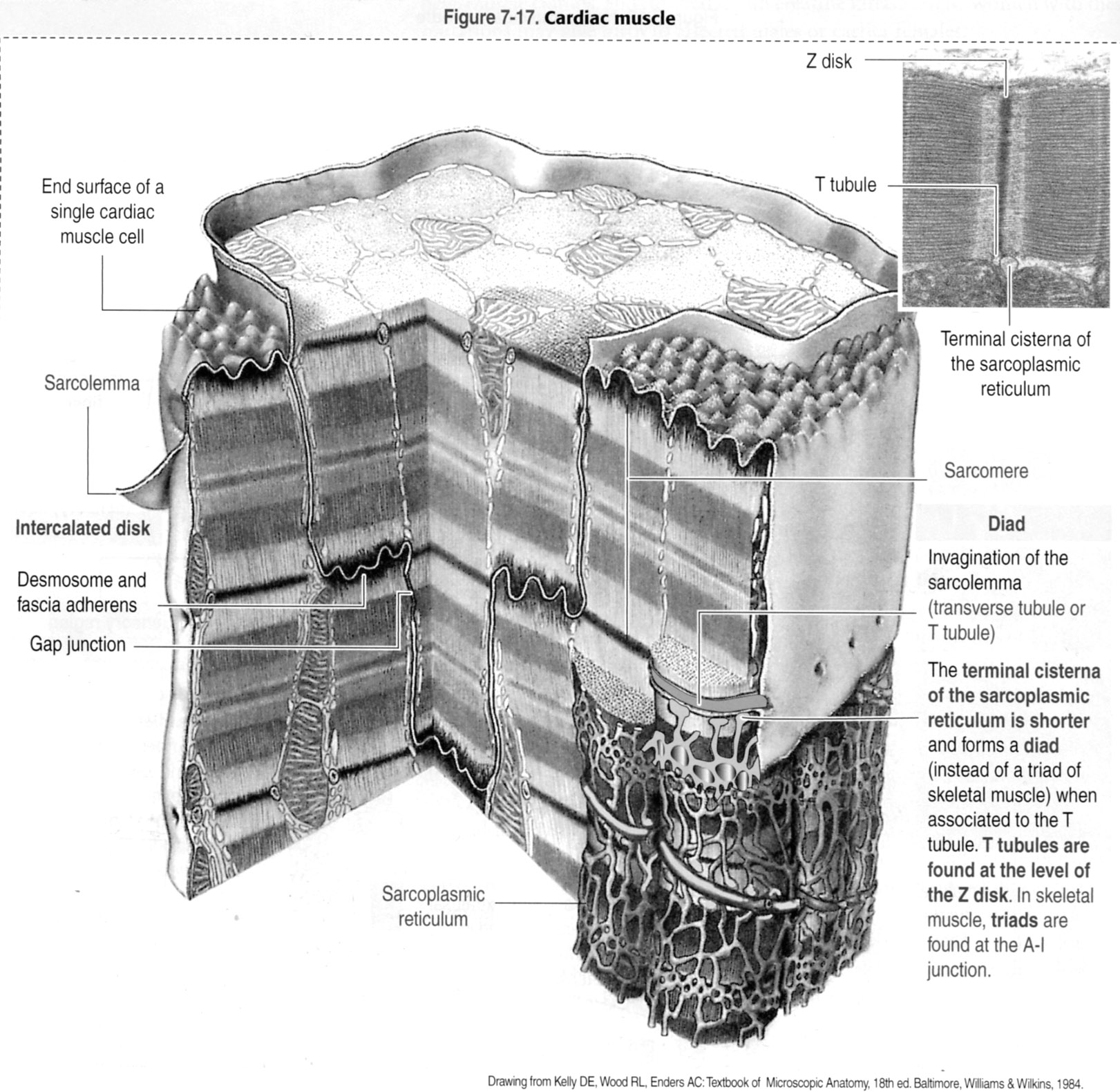 |
The diagram is fully labeled. |
| |
Intercalated Disk (ventricle, cat) | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
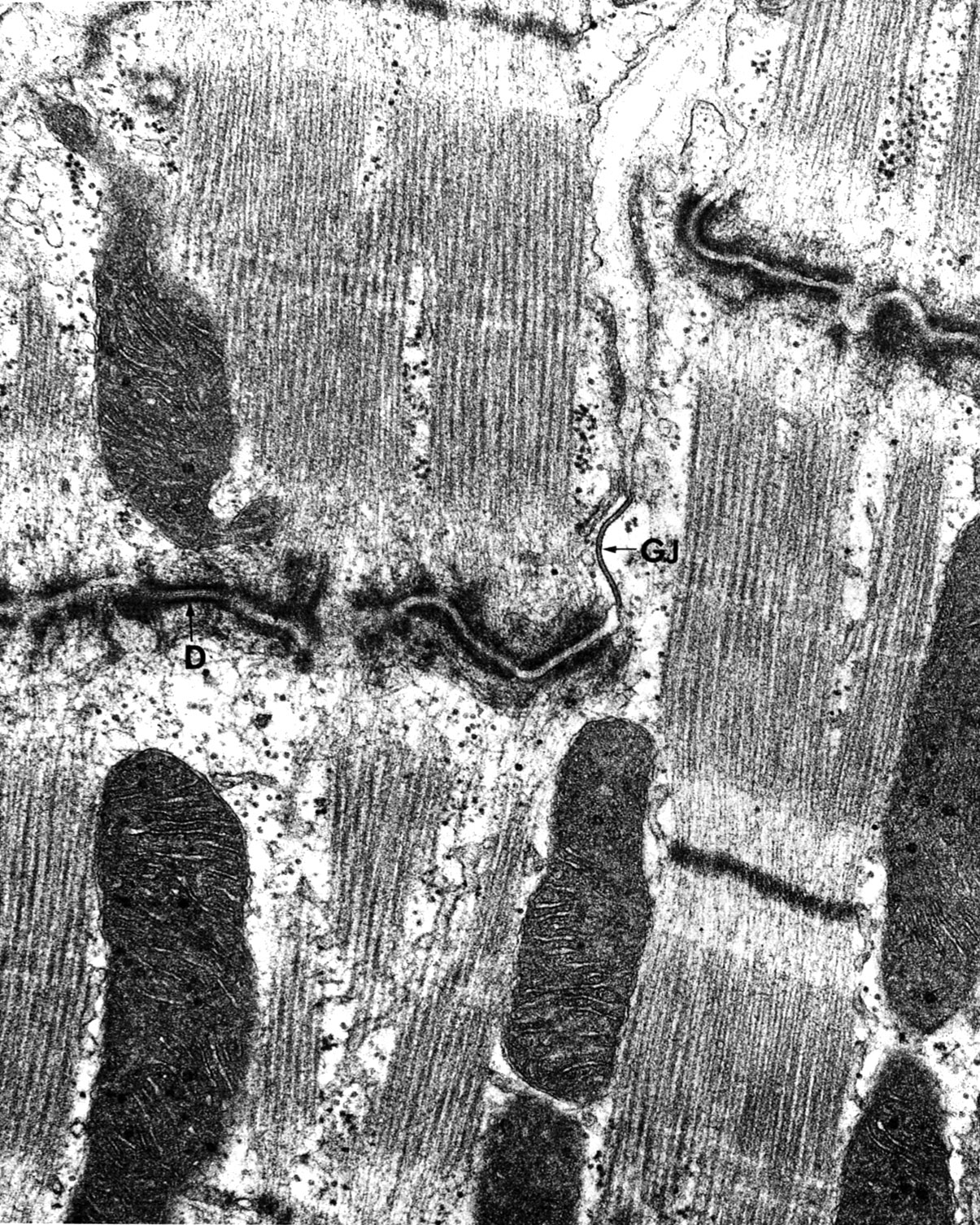 |
A gap junction (GJ) is present in the longitudinal portion of the disk. In the transverse portions, the actin filaments of the sarcomere insert into the filamentous web underlying the extensive fascia adherens junction. there are also occasional spot desmosomes (D) I, associated with intermediate filaments (desmin in muscle). Note the abundant glycogen (small particles) and the large mitochondria. |
| |
Smooth Muscle | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
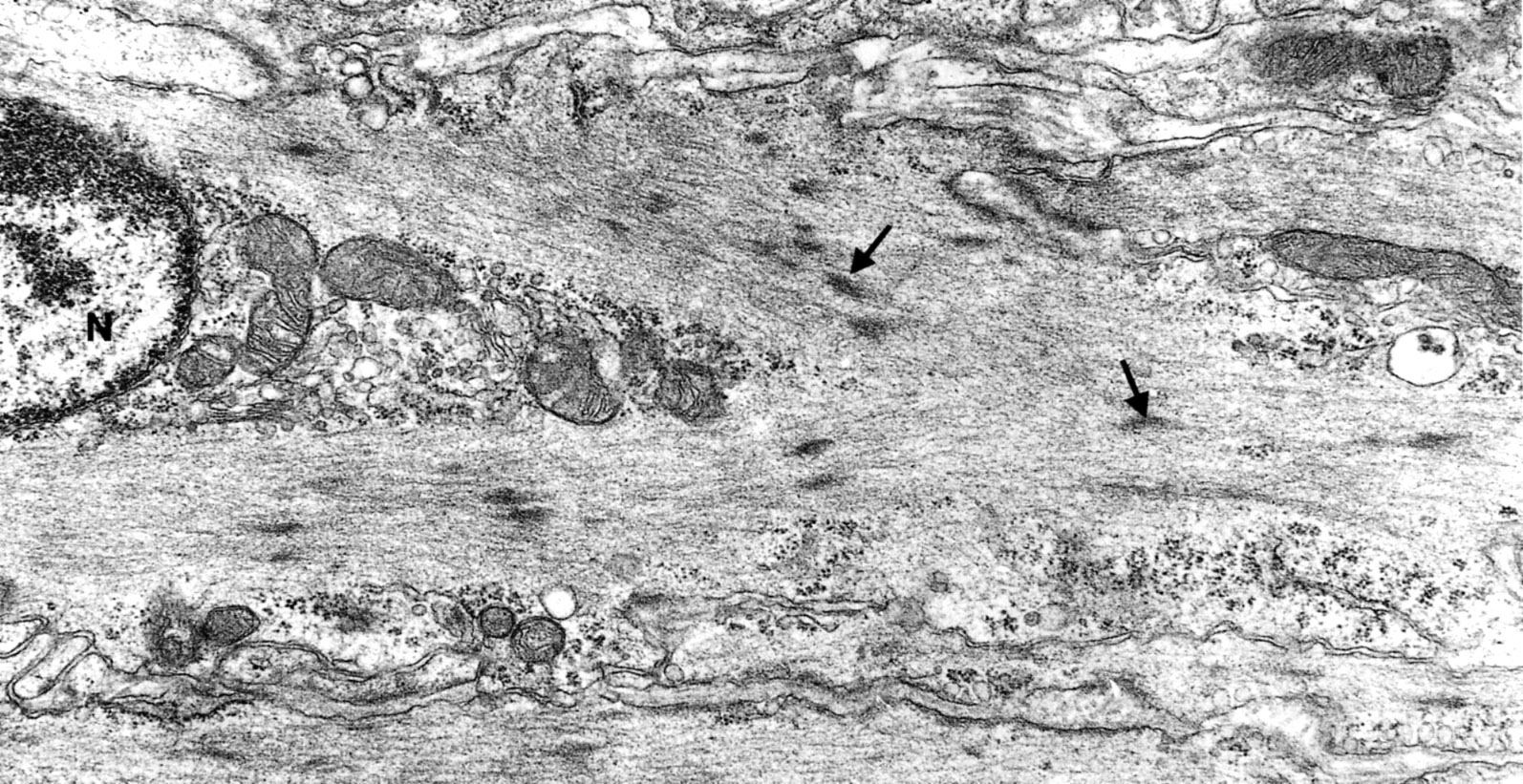 |
Longitudinal section of portion of smooth muscle fiber showing part of centrally located nucleus (N). Mitochondria, Golgi and ribosomes are abundant in conical perinuclear region. The remainder of the fiber is occupied by thin filaments and dense bodies (arrows) into which the filaments appear to insert. There are no transverse striations. (ileum of 13 day-old rat)
|
| |