SBPMD Histology Laboratory Manual
Epithelium: Simple Columnar Epithelia
#115 Gall bladder, Human. H&E
Open with WebViewer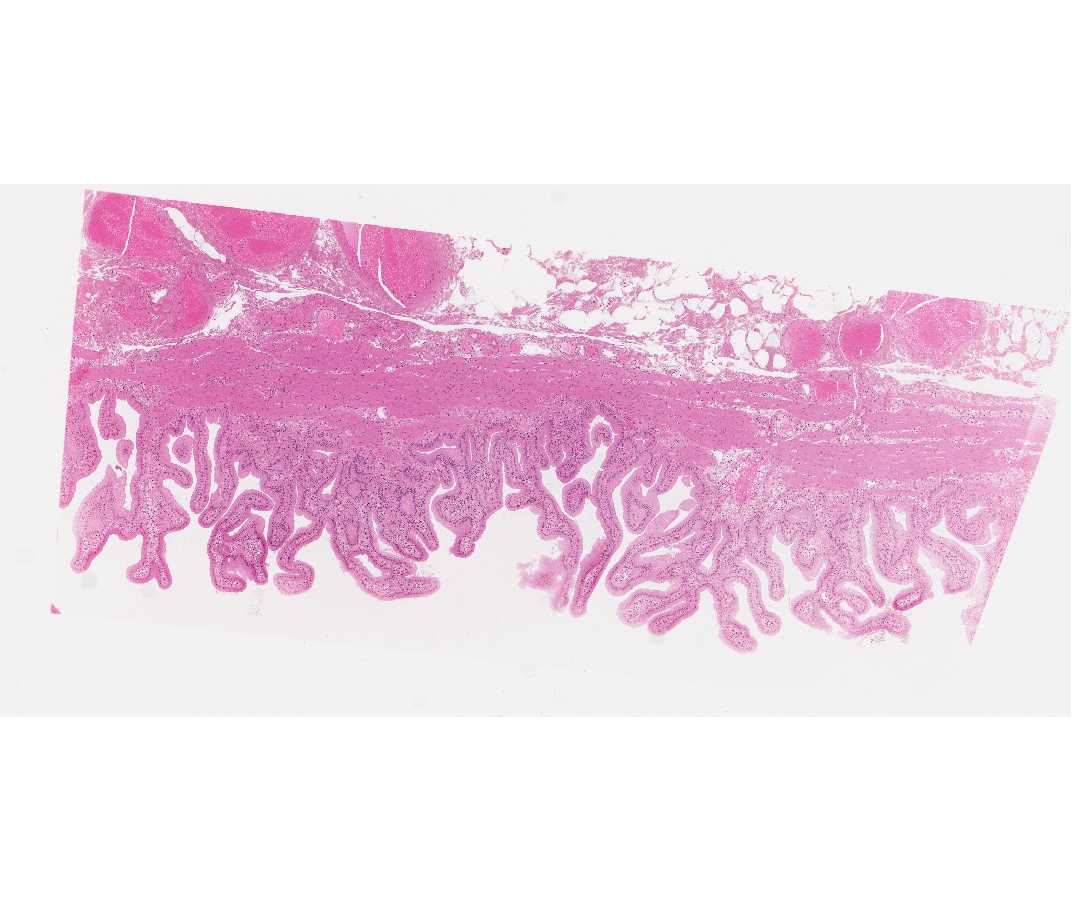
Examine the lining of the gall bladder as an example of simple columnar epithelium. Be sure you locate regions where the epithelium is cut longitudinally to observe the simple columnar epithelium. In tangential sections portions of cells in various planes of section may give the impression that the epithelium is stratified.
#102 Small intestine, guinea pig (Bodian/silver)
Open with WebViewer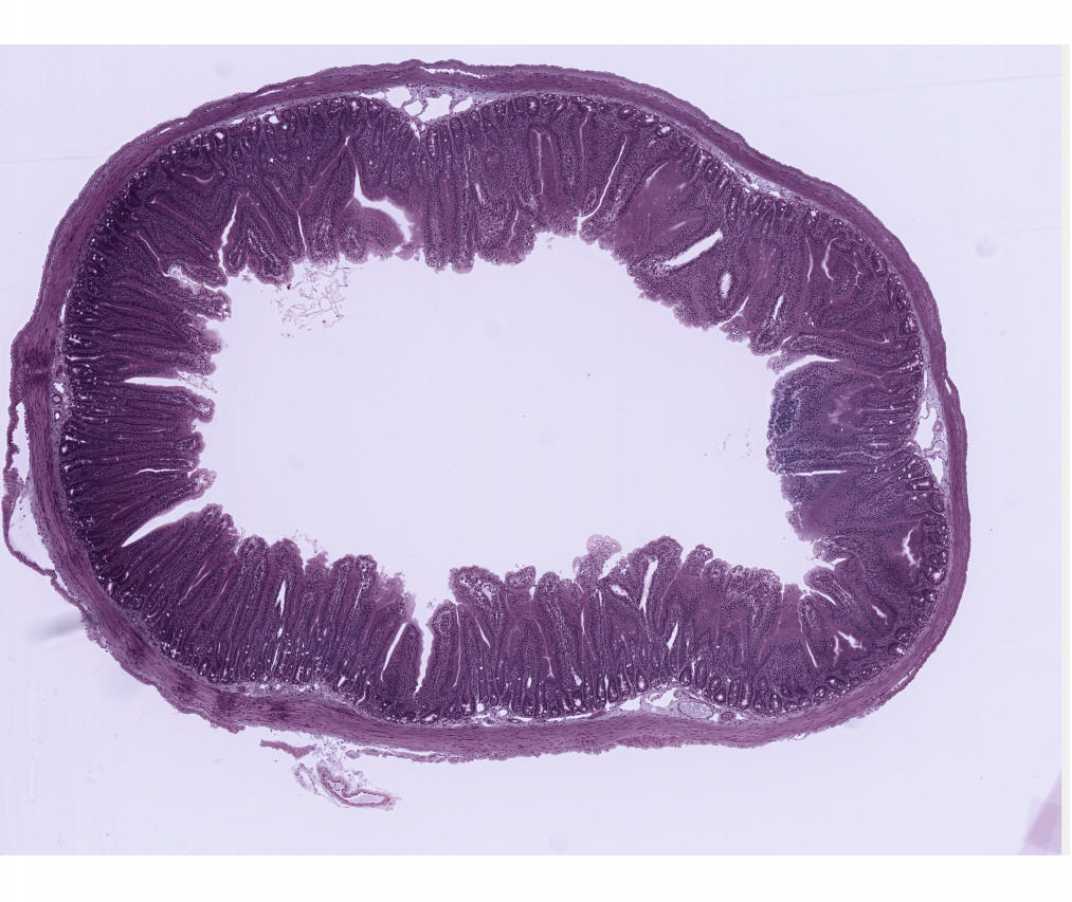
This slide illustrates modifications found in the apical region of the columnar epithelium: the striated (microvillous) border, and the terminal bar (junctional complex). In longitudinally sectioned cells, the terminal bar is seen as a dark dot of silver deposit at the apical lateral borders of the cells. In regions where the epithelium has been cut in cross or oblique section, the terminal bar has a belt-like appearance and can be seen to encircle the cells (hexagonal shape). Review the appearance of junctional complexes at the EM level in the electron micrograph in the lab.
In the villus absorptive cells, you may see under oil, a clear zone between the nucleus and apex of the cell; this is the Golgi area. Filamentous material, which probably represents mitochondria, is between the Golgi area and the terminal web region at the apex of the cell.
In addition the Bodian silver stains secretory granules within enteroendocrine cells in the epithelium and the basal lamina.
#101a Small Intestine. Guinea Pig (PAS and hematoxylin)
Open with WebViewer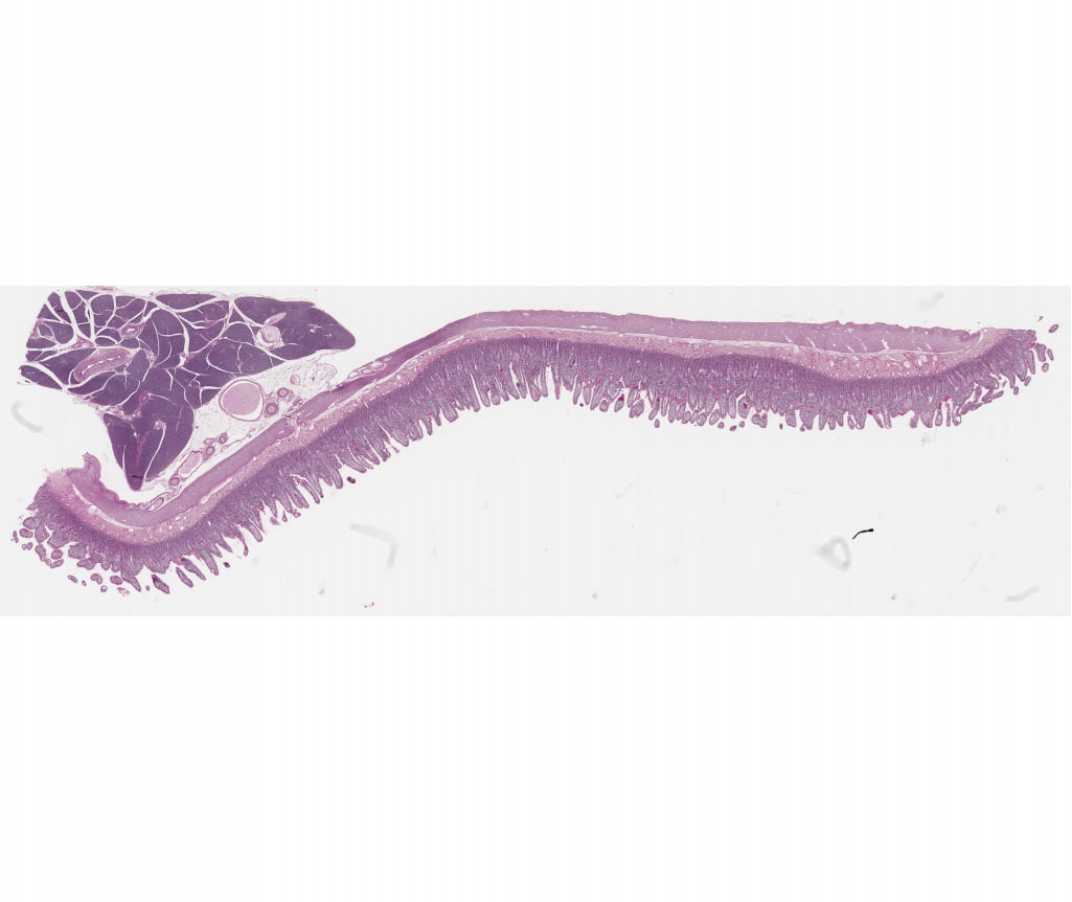
Locate the epithelium with its PAS positive glycocalyx. The basal lamina is also PAS positive, but is not intensely stained. Review the basis for PAS stain.
What types of intercellular junctions are commonly found in epithelia?