SBPMD Histology Laboratory Manual
Microscopy, Cells, Organelles, Mitosis: Micrograph
Examine the electron Micrographs so that you understand the ultrastructural equivalents of the structures you have seen under the microscope.
Secretory Cell | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
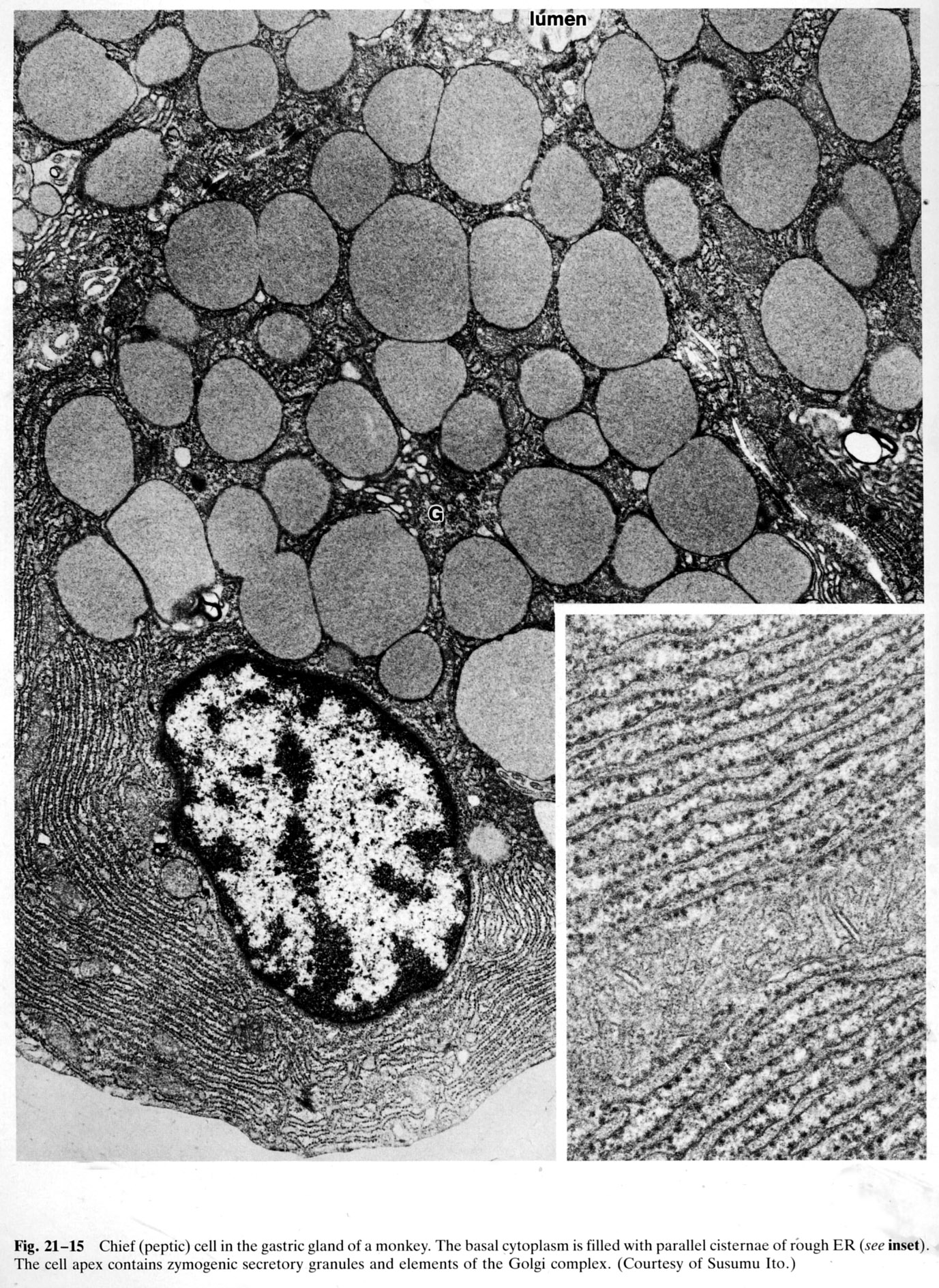 |
The basal cytoplasm is filled with parallel cisternae of rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and polyribosomes (see inset). The apex of the cell contains zymogenic secretory granules which are released into the lumen. Elements of the Golgi complex (G) are visible. (chief cell, gastric gland, monkey) |
| |
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum and Polyribosome Complexes | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
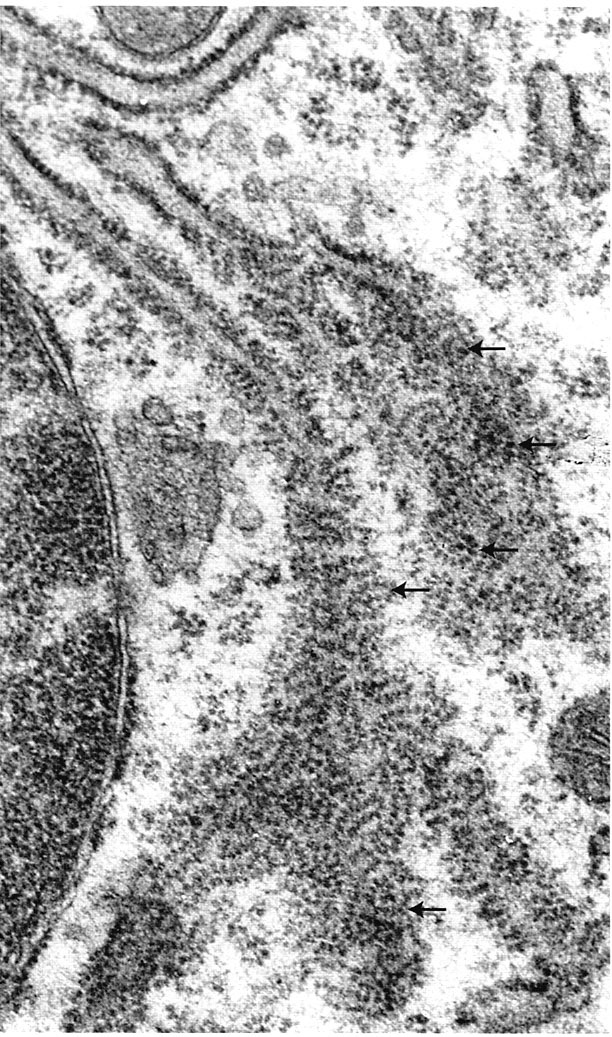 |
Small section of RER adjacent to the nucleus sectioned in two planes. The reticulum has turned within the section. In upper region membranes have been cut at right angles. In the center the reticulum has twisted. The large spiral cytoplasmic assemblies (arrows) are chains of ribosomes that form polyribosomes that are actively engaged in translation of the mRNA molecule. Ross MH and Pawlina W, Histology, 5th ed., Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, 2006, p. 45. |
| |
Plasma Cell | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
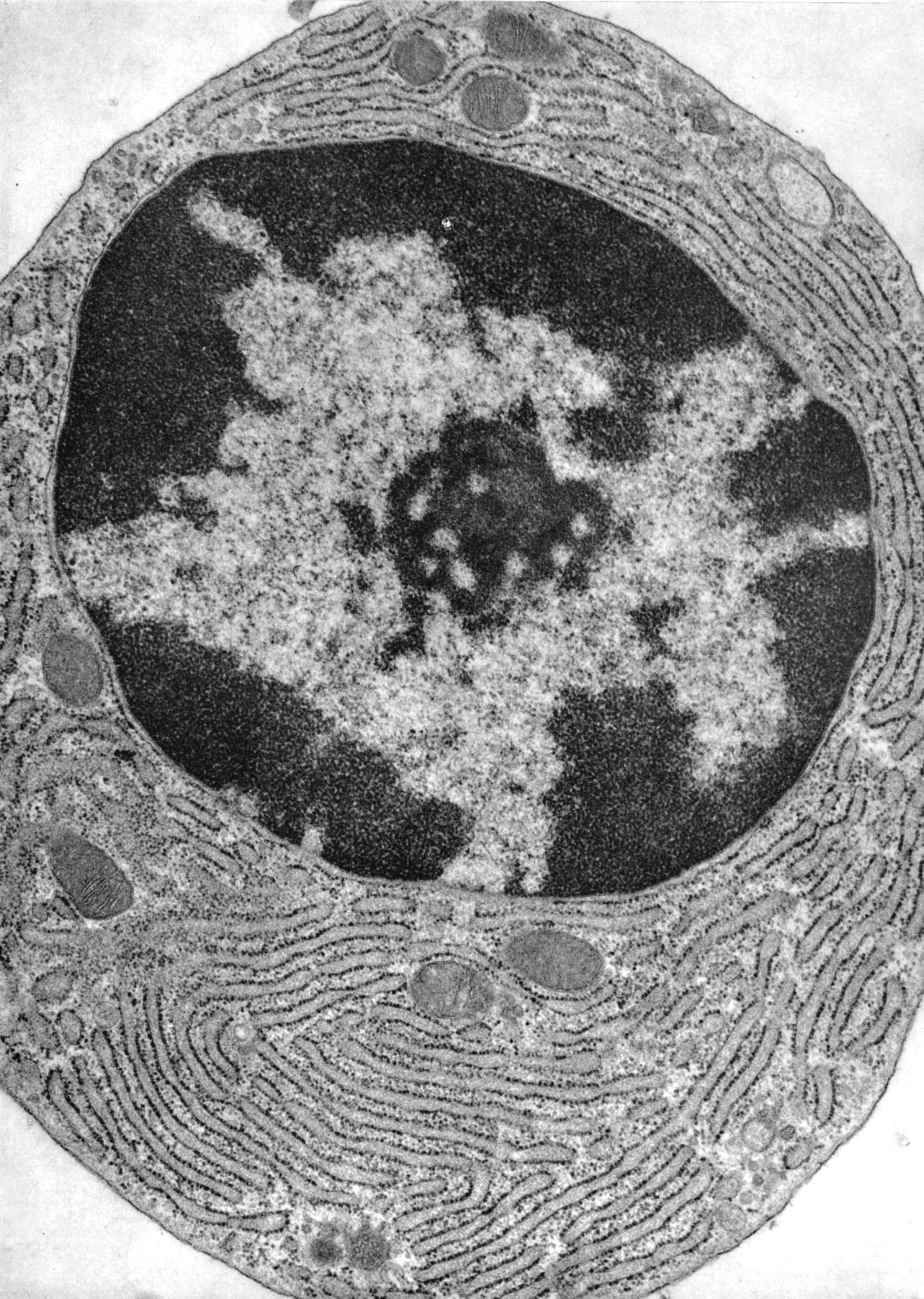 |
The plasma cell has an eccentric, largely heterochromatic nucleus with central nucleolus and heterochromatin clumped in a “clockface” or “wagon wheel” arrangement around the inner face of the nuclear membrane. There is extensive RER. Golgi complexes are typically visible. (bone marrow, guinea pig) |
| |
Junctional Complex | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
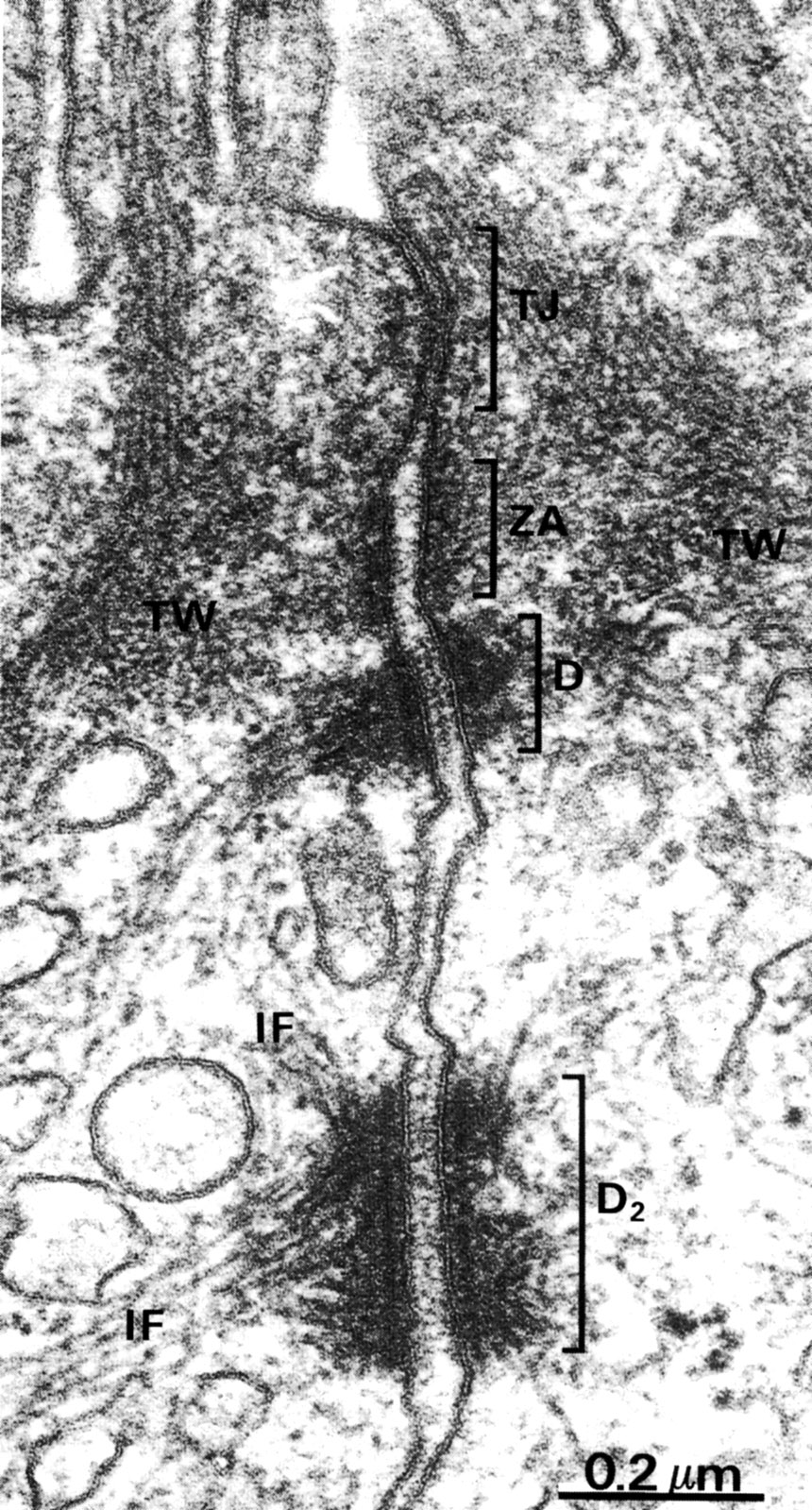 |
Apical region of two adjoining epithelial cells showing the junctional complex. This consists of the tight junction (TJ) also known as the zonula occludens, the zonula adherens (ZA) and desmosome (D1 and D2). Actin filaments insert into the zonula adherens and intermediate filaments(IF) insert into the desmosome. Actin filaments extend into the microvilli and form a component of the terminal web (TW) at the apex of the cell. |
| |
Microvilli | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
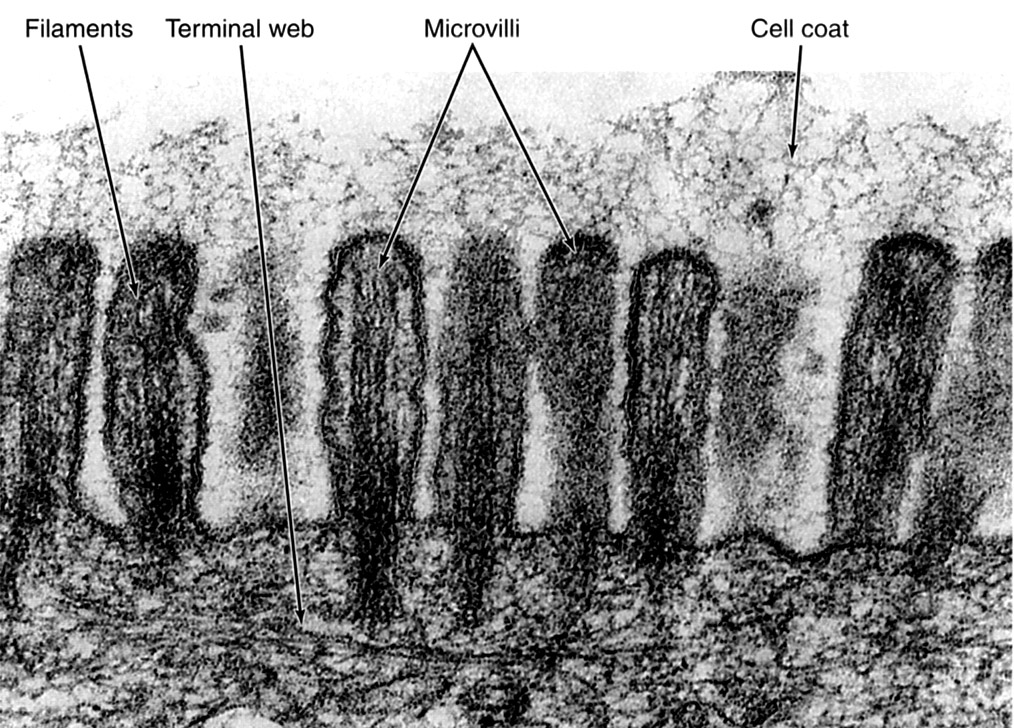 |
Microvilli are apical extensions of the cell that are filled with actin. An extracellular coat (glycocalyx) is bound to the plasmalemma of the microvilli. The terminal web is a network that contains actin filaments, intermediate filaments and spectrin. |
| |
Microvilli in Cross Section | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
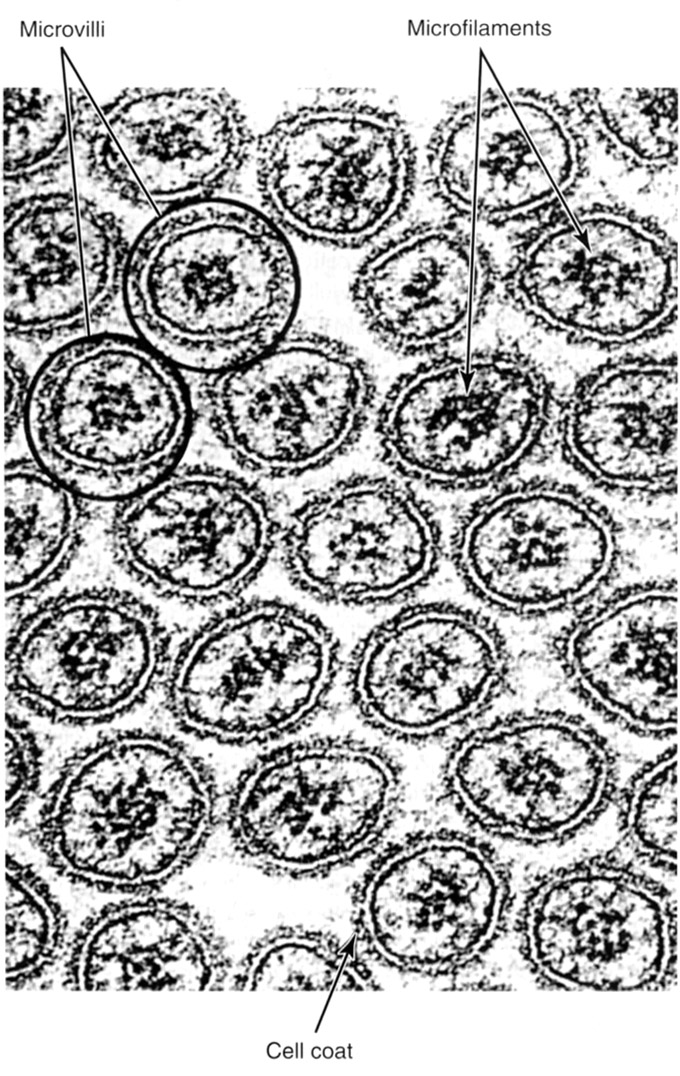 |
Cross sectioned microvilli in apical region of cell of intestinal lining showing cores of actin. Note the outsides of the microvilli are covered with a glycocalyx (cell coat). |
| |
Tracheal Lining with Ciliated Cells | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
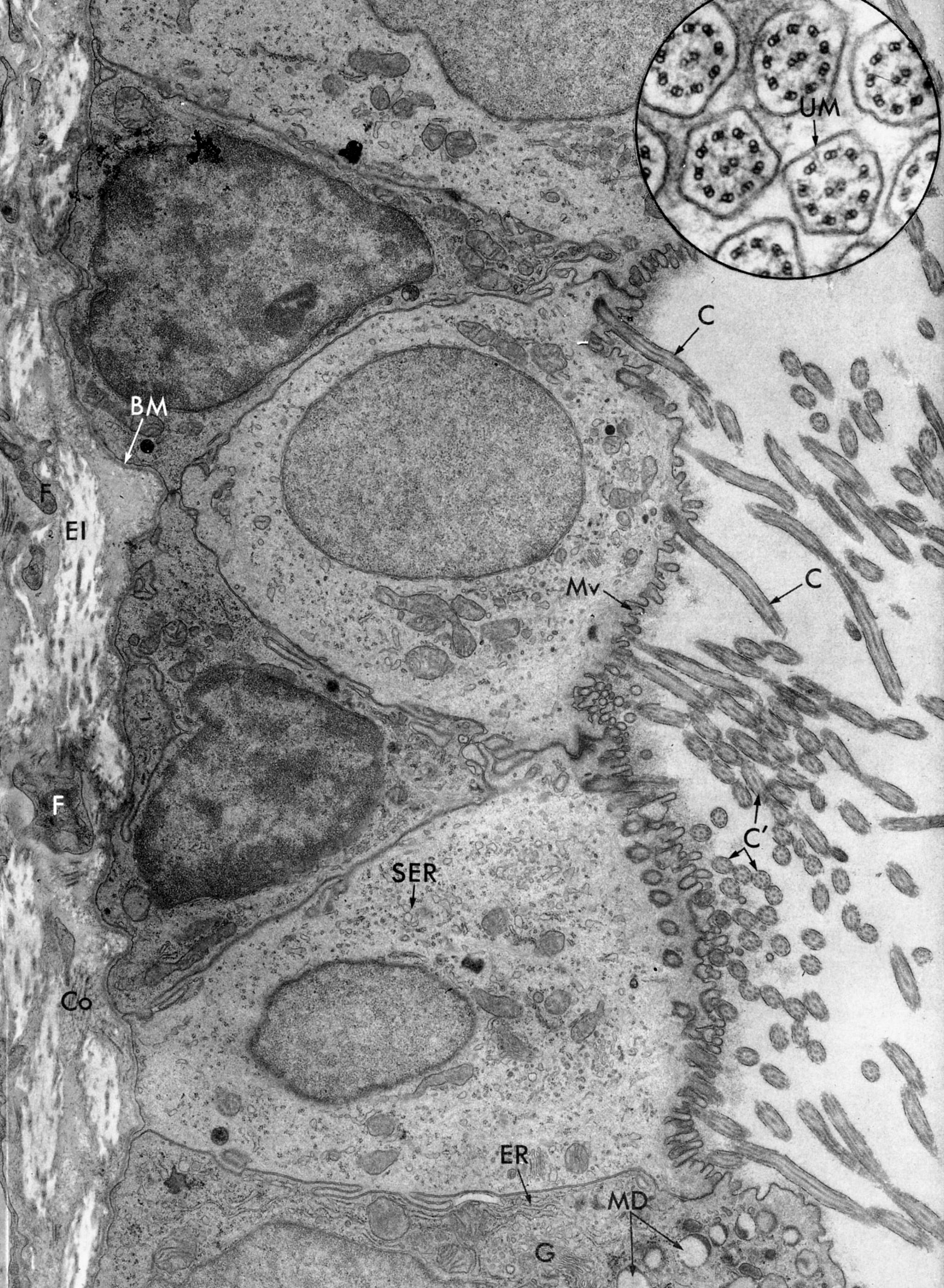 |
The ciliated cells have both microvilli (MV) and cilia, shown here cut in both longitudinal (C ) and cross sections (C’). Inset is cross sections of cilia, containing the axoneme (unit membrane ,UM). The goblet cell (bottom of micrograph) contains secretion droplets (MD) and organelles associated with elaboration of protein for export: (ER) and Golgi (G). The cytoplasm of the non-secretory ciliated cells contains scant Golgi and mainly smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). Fibroblasts (F), collagen (Co), elastic fibers (El). |
| |
Cilia | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
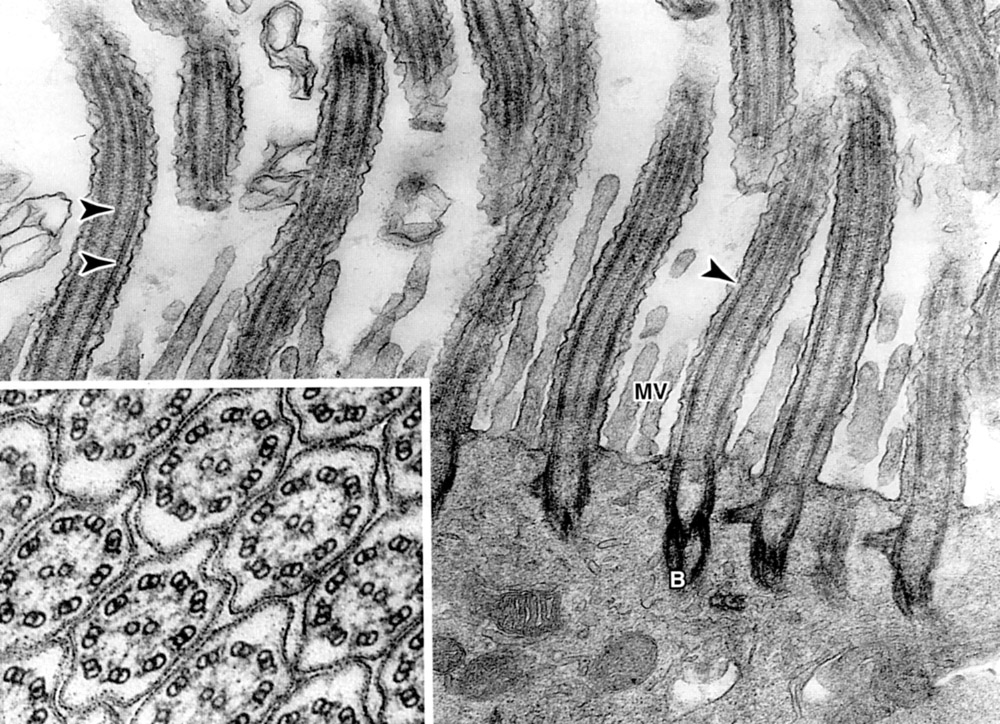 |
Apical portion of ciliated epithelium. Arrows (from left to right) indicate: central microtubule, peripheral microtubule of axoneme and plasma membrane. The axoneme comprises 9 peripheral microtubule doublets surrounding a central pair. Microvilli (Mv) are also present. Inset is cilia in cross section: Basal body (B). |
| |