SBPMD Histology Laboratory Manual
Cells, Organelles - Cellular Specializations
#117 Small intestine H&E.
Open with WebViewer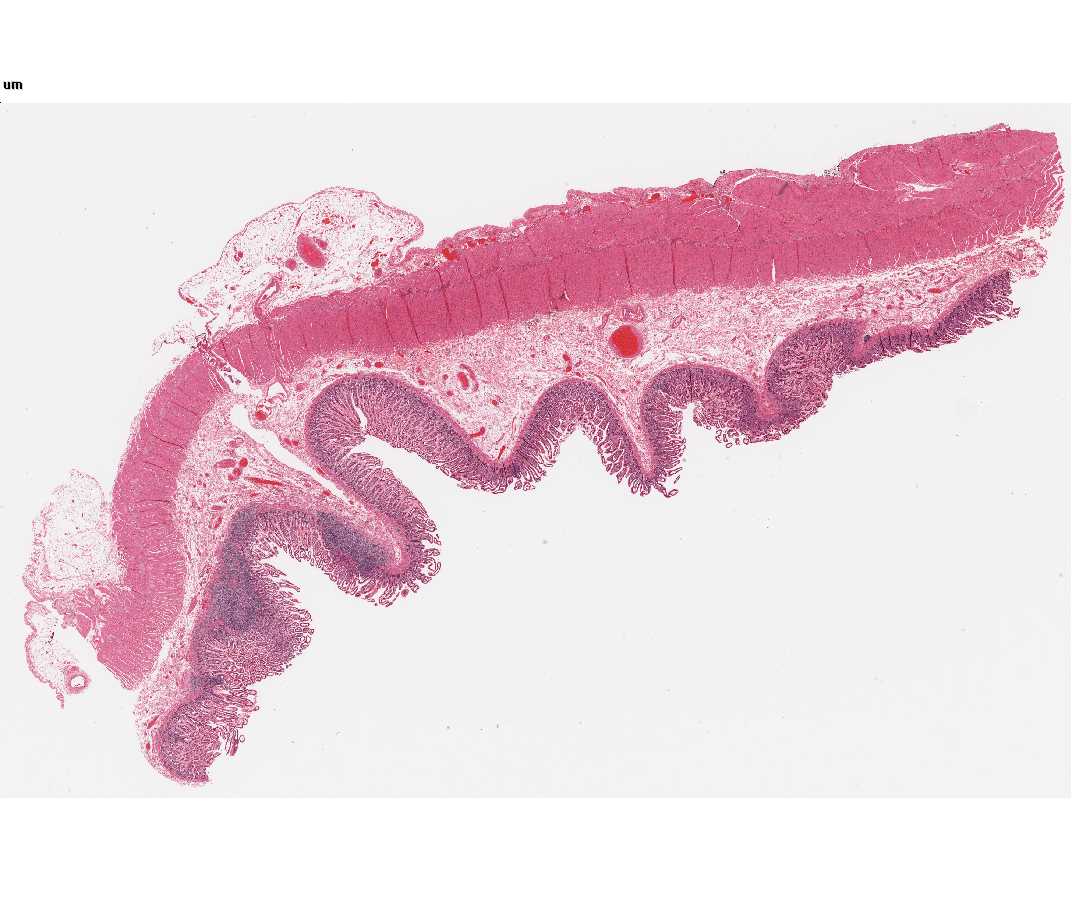
Study the cells lining the lumen of the small intestine. Confirm that the cells are columnar in shape and that their nuclei are basal in location. These are the villus absorptive cells. Goblet cells, ovoid in shape and less intensely stained, are dispersed among the columnar cells. At the apex of the columnar cell, i.e., that cell surface adjacent to the lumen of the intestine, a border may be identified which has slightly different optical properties from the remainder of the cell. Under optimum conditions faint striations, oriented parallel to the long axis of the cell, are seen in the border; it is unlikely that you will be able to resolve these striations with your microscopes. By electron microscopy, these striations are actually precisely arranged microvilli, containing cores of actin filaments.
#68 Oviducts (Fallopian tubes). Human H&E.
Open with WebViewer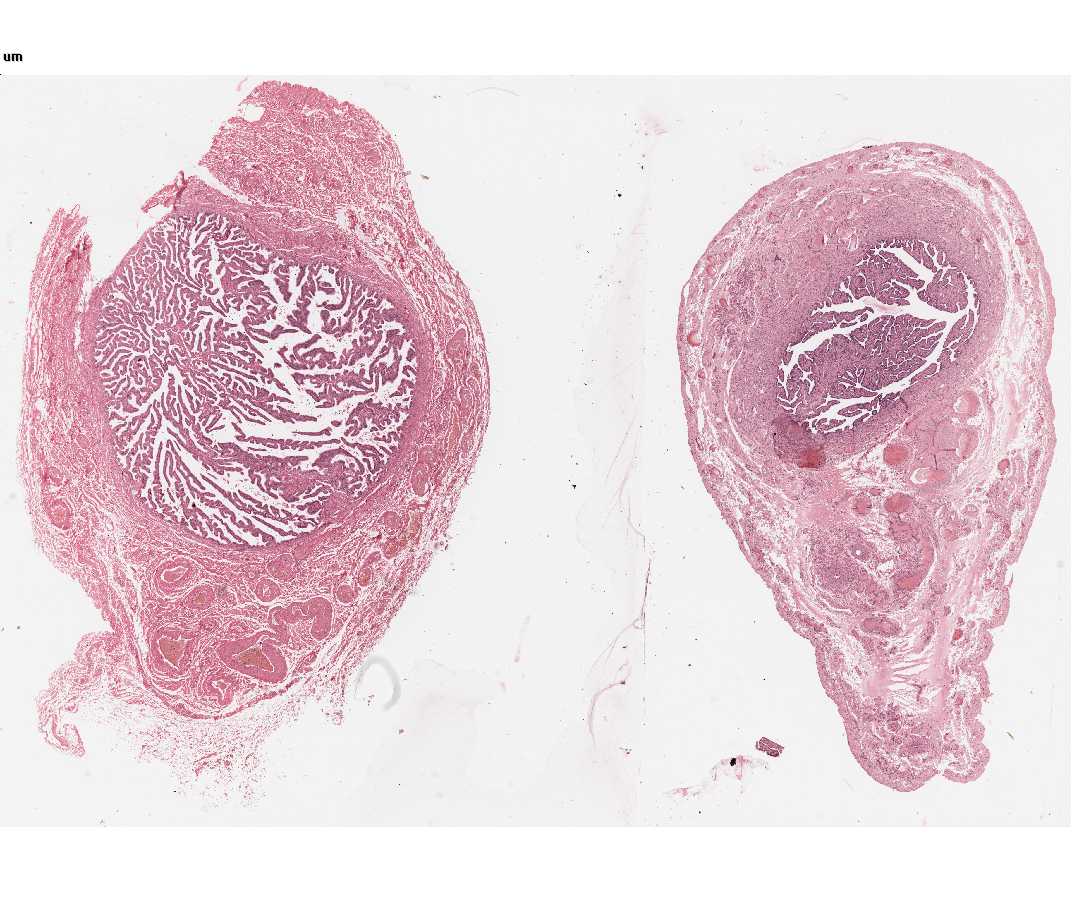
Locate the cells lining the lumen of the oviduct. Using the high dry and oil-immersion objectives, study the free surface of the cells. The majority have fine, hair-like projections called cilia. At the apex of these cells note the pink line, which indicates the presence of the basal bodies that give rise to the cilia. (Consult electron micrographs for the content and morphology of cilia and their basal bodies). There are also secretory cells along this epithelium. These have elongated nuclei and sometimes project above the epithelial surface